Foster Youth in California Schools
Information, resources, and educational outcomes for foster youth students.Students in foster care represent one of the most vulnerable and academically at-risk student groups enrolled in California schools. The California Department of Education (CDE) monitors the educational outcomes for foster youth and engages with multiple state agencies and non-profit organizations to ensure these students receive the supports and services they need. This web page provides information and resources related to foster youth in schools. Select one of the tabs below to access information on foster youth definitions or educational data and outcomes, among other resources, to learn more about the needs of these students and some of the different ways CDE is working to support counties, school districts, and schools to meet these needs.
Foster Youth Definitions
Different definitions of children and youth in foster care are used in relation to programs, services, educational entitlements, and programmatic funding supporting foster youth in schools. These definitions can vary at both the state and federal levels. The foster youth definitions included here are a small subset of the information available in the foster youth definitions resource document created by the CDE.
The Foster Youth Definitions(XLSX) document was created to describe which of the different entitlements, supports, and services are afforded to each of the categories of foster youth. The Foster Youth Definitions document is for reference purposes only, may not be comprehensive, and is subject to change depending on federal and state statutes and regulations. The table below and the Foster Youth Definitions document will be updated as needed.
| CATEGORY OF FOSTER YOUTH | Included in Local Control Funding Formula (LCFF) | Included in Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) | Included in CDSS' Definition of Care and Placement | CA Foster Youth Educational Rights | Available in California Longitudinal Pupil Achievement Data System (CALPADS) via Foster Match Process |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OUT-OF-HOME Child Welfare |
Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| OUT-OF-HOME Probation |
Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| IN-HOME PROBATION | Not Included | Not Included | Not Included | Yes | Not Available |
| FAMILY MAINTENANCE |
Yes | Not Included | Not Included | Yes | Yes |
| NON-MINOR DEPENDENTS | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| VOLUNTARY PLACEMENT AGREEMENTS |
Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| TRIBAL FOSTER YOUTH (AB 1962) | Yes | Only for Title IV-E tribes | N/A | Yes | In CALPADS, but not via Foster Match process |
| EMERGENCY REMOVALS | Not Included | Does not differentiate between emergency removal and placement | Yes | Yes | Yes (if in placement more than 7 days) |
Quick Facts
This tab provides quick facts displaying foster youth student data by program subgroup. Please visit the Foster Youth Data & Outcomes web page to access static data.
Statewide Student Enrollment Comparisons
2023–2024 Student Group Census Day Enrollment
The table below is calculated from census day enrollment data and includes the enrollment counts and percentage of statewide enrollment for each student subgroup included. Annual enrollment consists of the number of students enrolled on Census Day (the first Wednesday in October). Subgroup counts are not mutually exclusive and therefore do not sum to the report total. The table is modified from the DataQuest 2023–2024 Enrollment by Subgroup for Charter and Non-Charter Schools Report.
| Subgroup | Enrollment | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| English Learners | 1,074,833 | 18.4% |
| Foster Youth | 29,815 | 0.5% |
| Homeless Youth | 210,907 | 3.6% |
| Migrant Education | 45,329 | 0.8% |
| Students with Disabilities | 799,980 | 13.7% |
| Socioeconomically Disadvantaged | 3,659,382 | 62.7% |
| All Students | 5,837,690 | 100% |
For more information on foster youth enrollment and to access downloadable files, including both state- and county-level data, visit the CDE Foster Youth Enrollment by School Type Data web page.
For more information on cumulative enrollment and downloadable cumulative enrollment data files visit the CDE Cumulative Enrollment Data web page.
More information on the different school types in California’s public-school system can be found on the CDE File Structure: Public Schools and Districts web page.
Data & Outcomes
Identification of Foster Youth in the State Educational Data System
Foster youth are identified in schools through the statewide foster match process. This process matches California Longitudinal Pupil Achievement Data System (CALPADS) enrollment data to data from the California Department of Social Services (CDSS) CWS/CMS (Child Welfare System/Case Management System) data system.
Local Educational Agencies (LEAs) may also conduct local matches in CALPADS with their county welfare departments (CWDs). In this process, LEAs verify student demographic and enrollment data from local student information systems with data in CALPADS and manually match records in CALPADS using Case ID or Client ID from CWS/CMS.
Foster youth under the jurisdiction of a tribal court are identified separately from the match process between the CDE and the CDSS. These foster youth are identified by LEAs and that information is submitted to CALPADS through a program record (code 193). The Tribal Foster Youth Guidance Document(DOCX) provides guidance to LEAs on identifying tribal foster youth and reporting that information to CALPADS.
The Foster Youth Definitions(XLSX) document provides reference information specific to the data collection and reporting related to foster youth. This document is for reference purposes only, may not be comprehensive, and is subject to change depending on federal and state statutes and regulations.
Information on Foster Youth in CALPADS Foster Reports
LEA staff with appropriate security roles have access to the CALPADS 5.7 Foster Youth Enrolled – Student List report, which includes the following information on foster youth who have been identified through the CDE-CDSS weekly match process:
- School Code
- School Name
- Statewide Student Identifier (SSID)
- Student Name
- Local ID
- Date of Birth (DOB)
- Gender
- Ethnicity/Race
- ELAS Status
- Migrant ED status
- Students with Disability status
- Grade Level
- Enrollment Start Date
- Enrollment Status
- Local Match indicator
- Statewide Match indicator
- County of jurisdiction
- Service Type: An indication of whether the student is receiving family maintenance services (i.e., living at home) or in a placement, including voluntary placement agreements
- Client ID (10-digit)
- Case ID (19-digit)
- Case Start Date
- Episode Start Date (the start of the foster placement)
- Episode End Date (the end of the foster placement)
- Social Worker Name
- Social Worker Phone Number
- Responsible Agency (Child Welfare or Probation)
- Whether parental rights are limited (Y/N)
- Court Appointed Educational Representative Name
- Court Appointed Educational Representative Phone Number
- Last Update Date
LEA staff with appropriate security roles have access to the CALPADS Fall 1 1.18 – Free or Reduced Price Meal (FRPM) / English Learner / Foster Youth – Student List report which indicates enrolled students who have been identified as a tribal foster youth by the LEA and reported to CALPADS.
State Level Educational Outcomes of Foster Youth
The outcomes for foster students, outlined below, are published annually. These outcomes and more can be accessed on DataQuest. DataQuest is the California Department of Education’s online, public reporting system that provides reports about California’s schools and school districts. To find out how to access reports specifically for foster youth on DataQuest, view these Instructions on Accessing Data(DOCX).
2023-2024 Percent of Students Chronically Absent
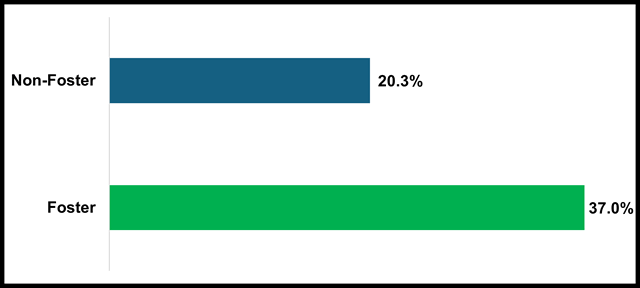
Chronic absence rate is calculated as the percent of students who miss 10 percent or more of the days they are expected to attend. In the 2023-24 school year, 37 percent of foster youth students in transitional kindergarten through grade twelve were chronically absent compared to a rate of 20.3 percent for non-foster students. Chronic Absenteeism reports are available through DataQuest.
2023–2024 Suspension Rate
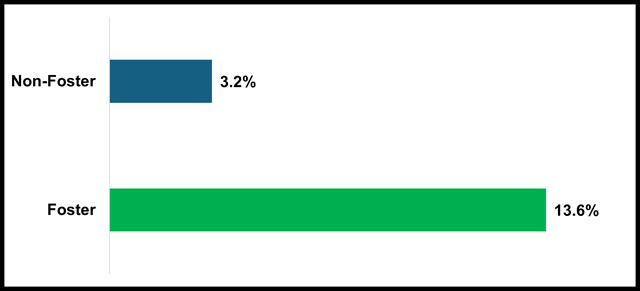
Suspension rate is calculated as the percent of all students who were suspended one or more times during the school year for an in-school or out-of-school suspension. In the 2023–24 school year, 13.6 percent of foster youth students were suspended for at least one day compared to a rate of 3.2 percent for non-foster students. Suspension reports can be accessed through DataQuest.
2023–2024 Four-Year Adjusted Cohort Graduation Rate
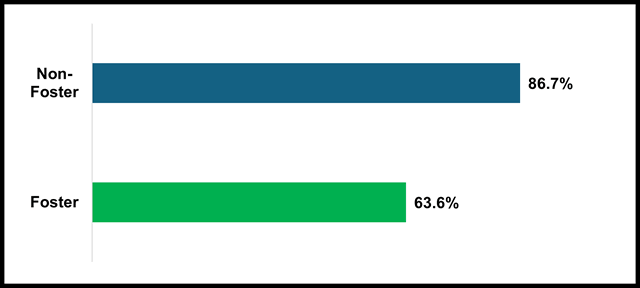
The four-year adjusted cohort graduation rate is calculated as the percent of students who graduate high school within four years from the time they enter ninth grade with a traditional high school diploma. The four-year cohort is based on the number of students who enter grade 9 for the first time adjusted by adding into the cohort any student who transfers in later during grade 9 or during the next three years and subtracting any student from the cohort who transfers out, emigrates to another country, transfers to a prison or juvenile facility, or dies during that same period. In the 2023-24 school year, 63.6 percent of foster youth students graduated compared to a rate of 86.7 percent for non-foster students. Four-Year Adjusted Cohort Graduation reports can be accessed through DataQuest.
2023–2024 Graduates Receiving a Local Requirements Exemption
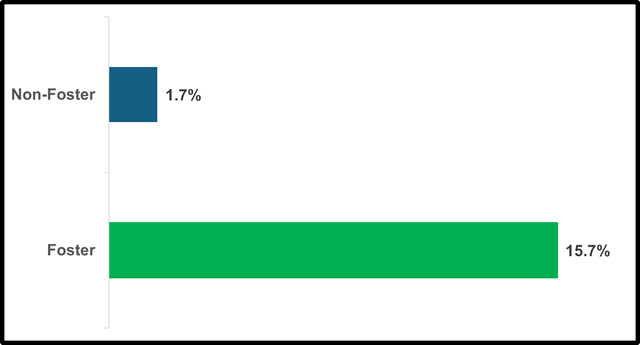
The Graduates Receiving a Local Requirements Exemption is a new indicator that shows graduating high school students who completed all state graduation requirements for a standard high school diploma but were exempt from local graduation requirements. For 2023-24, 15.7 percent of foster youth students graduated with an exemption from local graduation requirements compared to 1.7 percent of non-foster students. The Graduates Receiving a Local Requirements Exemption report can be found under the Four-Year Adjusted Cohort Graduation indicator and accessed through DataQuest.
2023–2024 Four-Year Adjusted Cohort Dropout Rates
The four-year adjusted cohort dropout rate is calculated as the percent of cohort students who (1) do not graduate with a regular high school diploma, (2) do not otherwise complete high school, or (3) are not still enrolled as a “fifth year senior.” In the 2023–24 school year, 24.9 percent of foster youth students dropped out compared to a rate of 8.7 percent for non-foster students. This data is included in the Four-Year Adjusted Cohort Graduation Rate Outcomes report available through DataQuest.
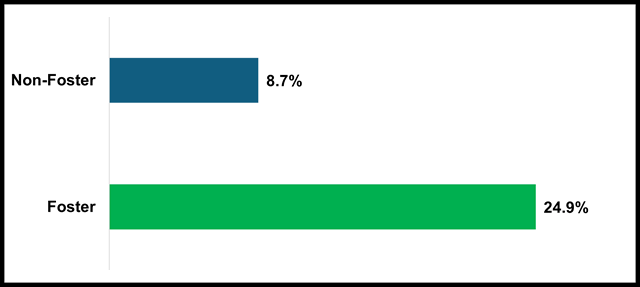
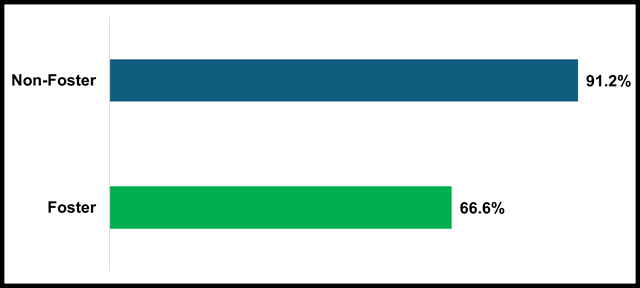
2023–2024 School Stability Rates
The stability rates are from a report that provides a total count of cumulatively enrolled students with an enrollment start date on or after July 1 and on or before June 30 (Adjusted Cumulative Enrollment), a count of students identified as part of the Stability Count (i.e., students with stable enrollments), and a count of students identified as part of the Non-Stability Count (i.e., students without stable enrollments). Students are determined to have a “stable” enrollment during the academic year if the enrollment record is a minimum of 245 consecutive calendar days at the same school without a disqualifying exit. The Adjusted Cumulative Enrollment along with the Stability and Non-Stability Count are used to calculate the Stability Rate (Stability Count divided by the Adjusted Cumulative Enrollment) and the Non-Stability Rate (Non-Stability Count divided by the Adjusted Cumulative Enrollment) at the selected entity for the selected population using the available filters. In the 2023–24 school year, 66.6 percent of foster youth students had a stable enrollment compared to a rate of 91.2 percent for non-foster students. This report is available through DataQuest.
Downloadable files, which include both state- and county-level data, can be accessed through the CDE Data and Statistics Student and School Data Files web page at Foster Youth Data Page.
More information on cumulative enrollment and downloadable cumulative enrollment data files can be accessed on the CDE Data and Statistics web page at Cumulative Enrollment Data Page.
More information on the different school types in California’s public school system can be found on the CDE Data and Statistics web page at Public Schools and Districts File Structure Page.
State Level Accountability for Foster Youth
This tab provides the latest statewide accountability indicators for foster youth.

California's accountability system is a multiple measures system that assesses how local educational agencies (LEAs) and schools are meeting the needs of their students. Performance on these measures is reported through the California School Dashboard
![]() .
.
The California School Dashboard (Dashboard) includes Performance Levels (or colors) for state indicators, which are determined using current year performance (or Status) and the difference from prior year (or Change) to show growth or decline. This results in five color-coded Performance Levels for each indicator. From highest to lowest, the Performance Levels are: Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange, and Red. For more information, please visit the Five-By-Five Colored Tables web page.
The 2023–24 accountability measures and historical foster youth performance can be found on the California School Dashboard
![]() .
.
For more information, resources, and guidance for the Dashboard and System of Support, please visit the California School Dashboard and System of Support web page.
English Language Arts
This measure of the Academic Performance state indicator reports student progress on the statewide assessment for English Language Arts/Literacy. It uses the Smarter Balanced Summative Assessments and California Alternate Assessments, and it is calculated based on the average "Distance from Standard" for all students in grades 3 through 8 and/or grade 11. The foster youth student group has a ‘Red’ performance level, ‘Maintained’ the level by 1.9 points, and scored 87.3 points below standard compared to the statewide average of 13.2 points below standard for all students. This data is available on the California School Dashboard
![]() .
.
Number of Students: 16,695
Mathematics
This measure of the Academic Performance state indicator reports student progress on the statewide assessment for mathematics. It uses the Smarter Balanced Summative Assessments and California Alternate Assessments, and it is calculated based on the average "Distance from Standard" for all students in grades 3 through 8 and/or grade 11. The foster youth student group has a ‘Red’ performance level, ‘Maintained’ the level by 2.3 points, and scored 125.1 points below standard compared to the statewide average of 47.6 points below standard for all students. This data is available on the California School Dashboard
![]() .
.
Number of Students: 16,733
Chronic Absenteeism
The Chronic Absenteeism state indicator shows how many students in transitional kindergarten through eighth grade were absent for 10 percent or more of the total instructional school days each student was expected to attend. The foster youth student group has an ‘Yellow’ performance level and ‘Declined’ by 3.1 percent. 30.5 percent of foster youth students in transitional kindergarten through eighth grade were chronically absent in the 2023-24 school year compared to the statewide rate of 18.6 percent for all students. This data is available on the California School Dashboard
![]() .
.
Number of Students: 25,730
Graduation Rate
The Graduation Rate state indicator reflects the percentage of students who graduate with a regular high school diploma in four years or five years. The foster youth student group has a ‘Red’ performance level but ‘Increased’ by 2.5 percent. 65.7 percent of foster youth students graduated in the 2023-24 school year compared to the statewide rate of 86.7 percent for all students. This data is available on the California School Dashboard
![]() .
.
Number of Students: 5,936
College/Career
The College/Career Readiness state indicator shows how many students graduate from high school better prepared for college or a career. It uses many different college and career measures, such as completion of coursework, work experience, and exam results. The foster youth student group has an ‘Orange’ performance level and maintained at 1.4 percent. 13 percent of the foster youth student group are prepared for college or a career compared to the statewide rate of 45.3 percent for all students. This data is available on the California School Dashboard
![]() .
.
Number of Students: 5,614
Suspension Rate
The Suspension Rate state indicator reflects the percentage of students in transitional kindergarten through grade 12 who have been suspended at least once in a given school year. Students who are suspended multiple times are only counted once. The foster youth student group has an ‘Orange’ performance level and ‘Declined’ by 0.4 percent. 13.2 percent of the foster youth student group were suspended for at least one day compared to the statewide rate of 3.2 percent for all students. This data is available on the California School Dashboard
![]() .
.
Number of Students: 39,269
State Level Accountability for Foster Youth
As noted, California’s public-school accountability system is designed to reinforce the expectation that everyone can improve while also ensuring additional support is provided to LEAs that are struggling. It also includes an intentional focus on aiding in a manner that builds capacity of the LEA receiving assistance. Differentiated assistance is therefore intended not only to help the LEA address the underlying causes that led to its eligibility for assistance, but also to strengthen the LEA’s overall ability to evaluate the effectiveness of strategies and programs and adjust as appropriate. This approach equips the LEA to improve in areas that were not the focus of differentiated assistance and increases the likelihood that improvements will be sustained when the differentiated assistance ends. To be eligible for assistance, the same student group must meet the criteria in two different priority areas.
In the 2023–24 school year there were a total of 104 LEAs and 3 charter schools with priority areas met by the foster youth student group that were selected for assistance status of Differentiated Assistance. For more information on assistance status, visit the Local Control Funding Formula - Allocations & Apportionments (CA Dept of Education) web page in which you will find the following 2024 downloadable file:
2024 LCFF Assistance Status
2024 LCFF COE/District Assistance Status Spreadsheet(XLSX)
2024 LCFF Charter School Assistance Status Spreadsheet(XLSX)
Local Control Accountability Plan
In order to create a clear connection between an LEA’s performance and the planning process articulated in the LEA's Local Control Accountability Plan (LCAP), California Education Code (EC) Section 52064 was amended to include a requirement that an LEA that meets certain criteria include one or more specific goals in the LCAP focused on improving student outcomes of low-performing student groups and/or schools. The legislative intent of these requirements is two-fold: first, to ensure that LEAs address the needs of consistently low-performing student groups; and second, to ensure that higher performing LEAs address the needs of low-performing schools within the LEA. There are 38 LEAs that must include a specific goal for foster youth in their LCAP in the 2023-24 school year.
The CDE has prepared files below that indicate the LEAs that have met the criteria to include one or more specific goals in the LCAP.
LCAP Required Goals Lists
LEAs required to include a goal in the 2023–24 LCAP based on student group performance(XLSX)
LEAs required to include a goal in the 2023–24 LCAP based on school performance(XLSX)
Education Rights of Foster Youth
Foster youth have unique needs and specific educational rights to support these students’ success in California schools.
A summary of the California Education Codes pertaining to foster youth is available on the Foster Youth Education Rights web page on the California Department of Education’s website.
Download the Foster Youth Education Law Fact Sheets created by the California Foster Youth Education Task Force (CFYETF) from the links below. These fact sheets are located on CFYETF's website and provide information on the needs and rights of foster youth in California schools.
California Foster Youth Education Law Fact Sheets in English(PDF)
![]()
California Foster Youth Education Law Fact Sheets in Spanish(PDF)
![]()
The Foster Youth Definitions(XLSX) document provides reference information on the educational supports and entitlements for foster youth. This document is for reference purposes only, may not be comprehensive, and is subject to change depending on federal and state statutes and regulations.
California Legislation on Foster Youth
This legislation, enacted in 2020, requires Foster Youth Services Coordinating Programs to coordinate efforts to ensure, to the extent possible, the completion of the Free Application for Federal Student Aid or the California Dream Act Application for foster youth pupils who are in grade 12.
This legislation was enacted in 2003 to address many of the barriers to equal educational opportunities for foster children and youth and expands and stipulates authority for school records of foster youth.
This legislation was enacted in 2013 to address high school graduation requirements for pupils in foster care.
This legislation enacted in 2015, also known as the Continuum of Care Reform bill, addresses foster care placement and foster care placement funding.
This legislation was enacted in 2015 to establish the Foster Youth Services Coordinating Program to coordinate and ensure that local educational agencies provide services to foster youth focused on positive educational outcomes.
This legislation enacted in 2018, also known as the Foster youth: trauma-informed system of care bill, requires each county to develop a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) to describe the roles and responsibilities of certain entities that serve youth in foster care who have experienced severe trauma. The legislation also instructs the Secretary of California Health and Human Services and the Superintendent of Public Instruction to establish a joint interagency resolution team to implement and review aspects of the MOU.
More information on the education rights of foster youth can be found on the California Department of Education’s Foster Youth Services Program Resources.
Complete information on the educational rights of foster youth can be found on the California Legislative Information website
![]() .
.
Partnerships
Foster Youth Services Coordinating Program (FYSCP)
The FYSCP is a grant program for each county office of education to support interagency collaboration and capacity building, both at the system and individual student level, focused on improving educational outcomes for students in foster care.
Visit CDE's Foster Youth Services site for more information including an overview of the Foster Youth Services Coordinating Program, grantee information, and CDE contact information.
Visit Foster Youth Services Program Resources for links to many informational resources and agencies which support the FYSCP and the needs of foster youth.
California Department of Social Services (CDSS)
California legislation requires the California Department of Education, in collaboration with the California Department of Social Services, to share and, through a statewide match process, inform districts regarding which of their students are foster youth (either living at home receiving family maintenance services or in out-of-home placements) on a weekly basis so that these students can best be served and receive appropriate educational supports and services. This is done through a weekly statewide foster match process.
Visit the California legislative information website for more information on Education Code 49085![]() which defines the data sharing requirements between the CDE and the CDSS pursuant to Education Code 49085.
which defines the data sharing requirements between the CDE and the CDSS pursuant to Education Code 49085.
Other Partnerships and Organizations
The California Department of Education partners with multiple state and non-profit organizations to collaborate on the support of foster youth in California Schools. Below are links to some of these agencies’ websites with information on foster youth.
California Foster Youth Education Task Force![]()
California Department of Social Services![]()
Alliance for Children's Rights![]()
California Child Welfare Council![]()
California CASA - Court Appointed Special Advocates for Children![]()






